Payroll taxes form the backbone of employee compensation and government revenue in India. For employers, understanding these taxes ensures compliance, avoids penalties, and maintains trust with employees. This guide breaks down the mechanics of payroll taxes, from deductions to deposits, while highlighting how the Best HR Payroll Software like Timelabs streamlines the process. Whether you manage a startup or a large enterprise, mastering payroll taxes is non-negotiable.
What Are Payroll Taxes in India?
Payroll taxes refer to mandatory deductions from an employee’s salary and contributions made by the employer to fund social security, retirement, and health schemes. Unlike income tax, which is a direct tax on earnings, payroll taxes are statutory contributions governed by specific laws.

In India, payroll taxes primarily include:
- Provident Fund (PF)
- Employee State Insurance (ESI)
- Professional Tax (PT)
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on salary
These deductions appear on every payslip and require timely remittance to authorities. Using HRMS Software such as Timelabs automates calculations, reducing errors and ensuring accuracy.
Key Difference: Employee vs. Employer Contributions
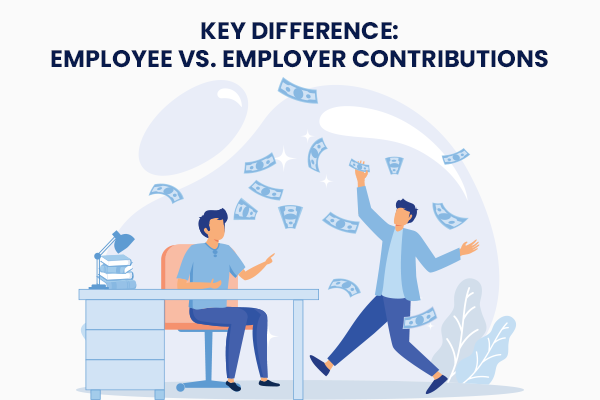
- Employee Contribution: Deducted from salary (e.g., 12% for PF).
- Employer Contribution: Additional amount paid by the company (e.g., 12% for PF + administrative charges).
This dual structure funds employee welfare while sharing the burden.
Major Components of Payroll Taxes
1. Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF)
Governed by the Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952, EPF applies to organizations with 20 or more employees.
Contribution Rates:
- Employee: 12% of (Basic Salary + Dearness Allowance)
- Employer: 12% (split as 8.33% to EPS, 3.67% to EPF) + 0.5% EDLI + admin charges
Ceiling:
- ₹15,000 per month (contributions on actual salary if higher, but pension limited to ceiling).
Compliance Deadlines:
- Deposit by 15th of the following month.
- File ECR (Electronic Challan cum Return) via EPFO portal.
Best HR Payroll Software like Timelabs generates ECR files automatically, eliminating manual uploads.
2. Employee State Insurance (ESI)
Regulated under the ESI Act, 1948, this applies to factories and establishments with 10+ employees (20+ in some states) where salary ≤ ₹21,000/month.
Contribution Rates:
- Employee: 0.75%
- Employer: 3.25%
Benefits:
- Medical care
- Sickness benefit
- Maternity benefit
- Disability compensation
Filing:
- Monthly contributions by 15th.
- Half-yearly returns by 11th May/11th November.
HRMS Software integrates ESI calculations with attendance data for precise deductions.
3. Professional Tax (PT)
A state-level tax levied on professions, trades, and employment. Rates vary by state and income slab.
Examples:
- Maharashtra: ₹200/month (₹300 for February)
- Karnataka: Up to ₹2,500/year
- West Bengal: ₹50–₹200/month
Key Points:
- Employer deducts and deposits to state treasury.
- Maximum ₹2,500/year across India.
Timelabs configures state-specific PT slabs, ensuring zero discrepancies.
4. Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on Salary
Under Section 192 of the Income Tax Act, employers deduct TDS based on:
- Employee’s income slab
- Declarations under Form 12BB (HRA, LTA, Section 80C, etc.)
- Projected annual income
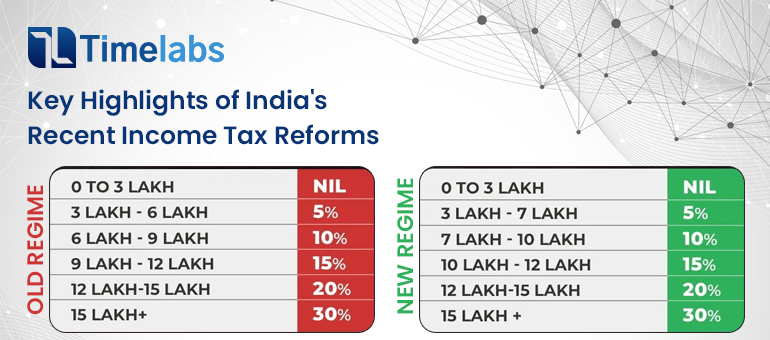
TDS Slabs (FY 2025-26, New Regime):
| Income Range | Tax Rate |
| Up to ₹3,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹3,00,001 – ₹7,00,000 | 5% |
| ₹7,00,001 – ₹10,00,000 | 10% |
| ₹10,00,001 – ₹12,00,000 | 15% |
| ₹12,00,001 – ₹15,00,000 | 20% |
| Above ₹15,00,000 | 30% |
Process:
- Estimate annual taxable income.
- Deduct monthly TDS.
- Deposit by 7th of next month (30th April for March).
- Issue Form 16 annually.
Best HR Payroll Software recalculates TDS dynamically with mid-year declarations.
Step-by-Step Payroll Tax Process
Step 1: Collect Employee Data
- PAN, Aadhaar, bank details
- Investment declarations
- Previous employment salary (Form 16 Part A)
Step 2: Compute Gross Salary
- Basic + HRA + Conveyance + Special Allowance + Bonus
Step 3: Calculate Deductions
Step 4: Generate Payslips
| Component | Formula |
| PF | 12% of (Basic + DA) |
| ESI | 0.75% (employee), 3.25% (employer) |
| PT | State slab |
| TDS | Based on slab after exemptions |
Include:
- Earnings
- Deductions
- Net Pay
- YTD figures
Employee Self Services portals in Timelabs allow 24/7 payslip access.
Step 5: Remittance & Filing
- PF/ESI: 15th
- TDS: 7th
- PT: State-specific
Step 6: Year-End Compliance
- Form 16
- Form 24Q (TDS returns)
- PF annual returns
Common Payroll Tax Challenges & Solutions
How Timelabs Simplifies Payroll Taxes
| Challenge | Solution with Timelabs HRMS Software |
| Mid-year joiners/leavers | Auto pro-rata PF/ESI/TDS calculations |
| Variable pay components | Configurable earnings heads |
| Multi-state operations | State-wise PT, bonus, leave rules |
| TDS projection errors | Real-time investment tracking via Employee Self Services |
| Audit trail gaps | Immutable logs and version control |
As the Best HR Payroll Software, Timelabs offers:
- 100% Statutory Compliance: Auto-updates for budget changes.
- Zero-Touch Processing: From attendance to tax filing.
- Employee Self Services: Update investments, download payslips, apply leaves.
- Seamless Integrations: Tally, SAP, biometric devices.
- AI-Powered Reconciliation: Flags discrepancies instantly.
With Timelabs HRMS Software, payroll processing time reduces by up to 80%.
Payroll Tax Calendar (Monthly)
| Date | Task |
| 7th | TDS deposit (previous month) |
| 15th | PF/ESI deposit & ECR |
| 20th | PT deposit (some states) |
| Last Day | Salary credit |
Advanced Scenarios
1. Bonus Payment
- Taxed at flat 30% if paid separately.
- Include in monthly TDS if clubbed with salary.
2. Arrears Processing
- Recalculate TDS for past months.
- Adjust in current payslip.
3. Expatriate Employees
- DTAA benefits
- Social security agreements (SSA)
Timelabs supports expat payroll with currency conversion and SSA mapping.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
| Act | Penalty |
| EPF | 12–25% p.a. interest + levy |
| ESI | 12% p.a. + imprisonment up to 1 year |
| TDS | 1.5% p.m. interest + ₹200/day (Section 234E) |
| PT | ₹5/day (Maharashtra) |
Best Practices for Employers
- Onboard with Compliance Checklist: Verify PAN, Aadhaar, UAN linking.
- Encourage Employee Self Services: Reduce HR queries by 60%.
- Conduct Quarterly Reconciliation: Match Form 26AS, PF passbook, ESI TI portal.
- Use Cloud-Based HRMS Software: Real-time access, disaster recovery.
- Train HR on Budget Changes: Annual finance bill updates.
Must Read: Breaking the Myth: Why Mid-Year Payroll Software Migration Is Easier Than You Think
FAQs
Q1. Is EPF mandatory for all employees?
Ans: No. Mandatory for salaries ≤ ₹15,000/month in eligible organizations. Higher salaries can opt voluntarily.
Q2. Can an employee opt out of ESI?
Ans: Yes, if salary exceeds ₹21,000/month or via Form 1 declaration (conditions apply).
Q3. How does Timelabs handle TDS on perks?
Ans: Configurable FBT rules with auto valuation (e.g., car, accommodation).
Q4. What if an employee submits investment proofs after the deadline?
Ans: Employee Self Services allows mid-year updates; Timelabs recalculates TDS instantly.